A Beginner's Guide to Authentication
Authentication is the process of uniquely identifying an individual via a set of credentials. In the digital world, authentication is termed as verifying a person's identity or an electronic device. Authentication becomes necessary because it increases the security of consumer's data. Without verifying or authenticating oneself, no one can enter the website and access your data. The most popular example of authentication is entering into a system using login credentials. With the huge increase in the number of digital platforms, the demand for various authentication processes has been increasing for both online and physical systems.
What is Authentication
We all have witnessed a spike in online user platforms from the past few years, catering to every service you can think of. This is because making things digitally available has eased the consumer’s struggle. For example, now you can order your food just by logging in to a food catering website. Easy, right? Everything is now just a click away. Your banking transactions, business, things of entertainment like movies and Netflix. Everything! But with all these services comes a massive task for the service providers, and that task is to verify that you are their actual consumer and not an imposter trying to steal data. So, to verify users, businesses use a technical approach called authentication.
How Does Authentication Work
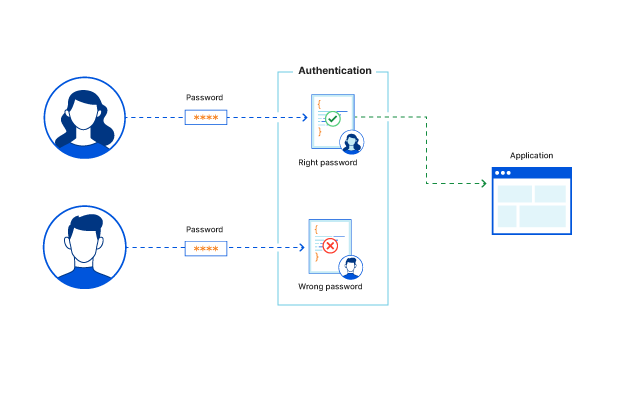
As mentioned above, the consumer needs to create a unique user ID and password at registration. The system will use this data to validate the consumer whenever they attempt to log in next time. These credentials will be stored in the companies database or on the local operating system through an authentication server. Now when the consumer enters these credentials on login, the entered credentials are matched with the ones stored in the database. If the credentials match, the consumer is given access into the portal; else access is denied. Now the question comes how to create such credentials which can be remembered easily? There are a few ways that can help you in simplifying your validation. These ways are: 1. Things you know (knowledge): This method involves questions that only you can answer. What is your mother's maiden name? Or what is your child's name? The purpose is to verify your identity via these questions because you are the only one who can answer these. 2. Things you have(possession): This method involves verification from the things you have or possess, such as a mobile phone. A verification notification will be sent to your phone screen, and when you allow it from that screen only, you will be able to log in to your account. 3. Things you are(inheritance): A fingerprint or retinal scan commonly verifies this factor. This method's purpose is clear; only you can have your fingerprint and no one else.
What are authentication factors?

Validating a user with a user ID and password is considered the most basic type of authentication. It depends on the user knowing those two pieces of information. Since this type of authentication relies on just one authentication factor, it's a type of SFA. Strong authentication is more reliable and resistant to attack. Typically, it uses at least two different types of authentication factors and often requires strong passwords with at least eight characters, a mix of lowercase and uppercase letters, special symbols and numbers. 2FA and MFA are types of strong authentication, with MFA among today's most common authentication practices. An authentication factor represents a piece of data or attribute that can validate a user requesting access to a system. An old security adage has it that authentication factors can be something you know, something you have or something you are. Additional factors have been proposed and applied in recent years, with location often serving as the fourth factor and time serving as the fifth factor.
Conclusion
In this article we have talked about the basics of authentication and how it is used. We have also covered how authentication works and what are the benefits to the organizations.